This can sometimes happen on home networks, where you find that the Wi-Fi on your router is not working, but if you plug into the router with an ethernet cable, it seems to work fine. So wired connections work, but wireless ones don’t.
This can seem at bit strange when we encounter it – how can a router “half” work? But there are sometimes reasons why this happens that we can identify and solve with a bit of work.
If your router Wi-Fi is not working, but the ethernet is, you can try rebooting and updating your devices and router, and also moving closer for a better signal. Also ensure that Wi-Fi bands are enabled, and try switching bands on dual band routers. Factory reset your router as a last resort option.
These options can sometimes fix the problem, but other times, there’s something in the actual hardware/circuitry of the router itself that’s broken, in which case you’ll need a repair or replacement. We’ll provide some links to contact your ISP if this is the case, but let’s first look at all the things you can try yourself to get the Wi-Fi working again.
Try Some Quick Reboots, Resets & Updates
The first thing to try with this kind of Wi-Fi error is quick reboots of everything:
- Restart your devices
- Reboot your router
- Check for firmware updates on your router from the settings page.
- Make sure your devices are fully updated, especially with any network driver updates.
- As a last ditch resort you could try factory resetting the router to wipe all settings and faults and return the router to it’s “out the box” state. See section below on this.
These are more obvious steps, but sometimes just rebooting devices can refresh the wireless connection and restore network access.
Check & Improve Wi-Fi Signal Strength
This is another thing to check early on, especially if your devices are trying to use the Wi-Fi quite a long way from the router. It can be that plugging directly in close up works fine, but trying to connect over wireless at a distance doesn’t because the signal keeps failing. Try using Wi-Fi closer to the router to see if this is the case.
If you find this is the case, then it’s a signal strength issue. Move your devices closer to the router, removing any obvious obstructions like walls, floors etc, and also away from any electrical devices that might interfere with it, like microwaves etc.
Obviously this is easier said than done in a lot of cases, but you can also consider using Wi-Fi boosters/extenders to improve the signal in the home. Also check out the powerline adapter solution further below for a way of bypassing Wi-Fi altogether even when a long way from the router.
Make Sure Wi-Fi Bands Are Enabled
This can be the case if you’ve just moved into a rented/vacation property, or any other Wi-Fi network you don’t normally use. You might not be able to find the Wi-Fi networks because they aren’t enabled, but you can still plug in with a LAN cable.
But you can enable them from the router settings. Here’s how:
- Make sure your device is connected to the router. Plug in with a LAN cable if the Wi-Fi doesn’t work at all, even at close range.
- Log into your router, using it’s IP address, admin/username and password. IP is most commonly 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.1.254. Type this into the browser address bar of any device connected to the router. All login details can be found on a sticker on the back of the router.
- Once inside the router settings, you are looking for Wireless, Wireless Settings, or possibly Security.
- There should be an option somewhere on SSID Broadcast or Visibility. Or there might be a Bands option for dual band routers (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz).
- Make sure this option is set to On or Enabled, or the box allowing SSID Broadcast or Visibility is checked. Or there may be an option to Enable Wireless. Or make sure one or both bands are toggled on (like below).
- The Wi-Fi network(s) should now be active again – try finding them again on any device in range.
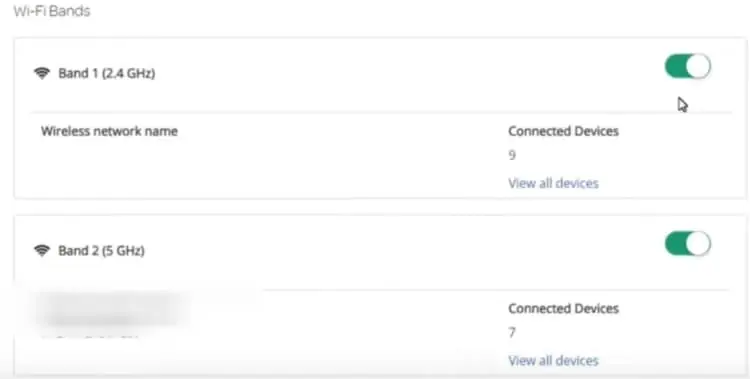
Try Switching Wi-Fi Bands
If you are sure the Wi-Fi networks are enabled and broadcasting, but just aren’t working well, and the router is dual band (has two networks), you can try switching to the other network to see if it gives a better signal.
This can be especially so if you’re trying to connect to to the 5 GHz band, which can be weaker over distance. Try connecting to the 2.4 GHz band instead – it often gives better performance over distance.
On dual band routers, you’ll find two network names (SSIDs) on the sticker on the back; one for 2.4 GHz and one for 5 GHz:

If both are enabled, then both should show up on the network list on your device.
Try connecting to the other band instead. It may give you a better signal.
Use a Powerline Adapter For A Wired Connection At Distance
If you can’t seem to get the Wi-Fi networks working at all, then one workaround solution that can be useful at least temporarily while you’re getting it sorted is to use a powerline adapter instead.
These are a pair of adapter plugs, one of which is connected to your router, and the other is connected to your device via LAN cables. The two plugs then communicate through the existing electrical wiring of the house to deliver a wired ethernet connection in any room it’s needed.
See the video below for a quick demonstration of how powerline adapters work.
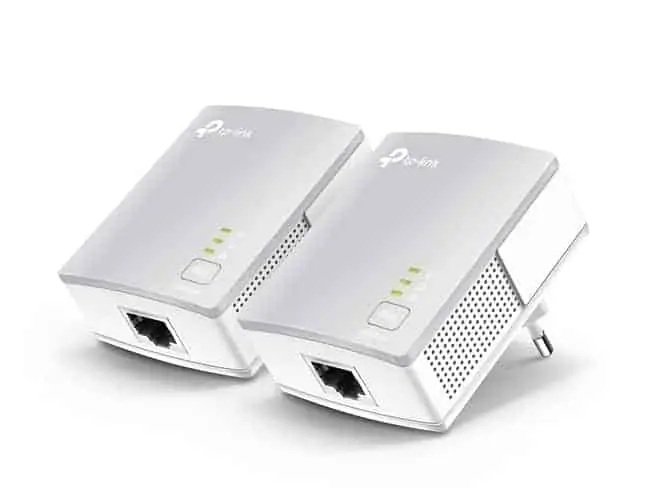

If you need to connect portable devices, then Wireless Powerline adapters are also available, that provide a cloned Wi-Fi access point at the receiving end as well as ethernet ports.
They can be a great way of bypassing Wi-Fi altogether if it isn’t working and transfer wired ethernet connections to any room in the house, even at distance from the router.
Some people might not be crazy about using these products long term, and they might not work in some houses, but they can provide at least a workaround while you’re getting your router repaired or replaced, if it turns out it’s broken (see below).
Factory Reset Your Router
This can be more of a last ditch effort if you’ve tried everything else and can’t get the Wi-Fi bands to work. There might be a fault or glitch in the router firmware which has disabled the Wi-Fi functionality, but for some reason left the ethernet ports working.
In this case a factory reset can wipe all settings, glitches and faults off the router and restore it to it’s “out the box” state, like when it first shipped new from the factory. All software will be reinstalled, which may fix any errors and allow the Wi-Fi to start working again.
On most routers, there’s simple reset button somewhere prominent, and also a reset/factory reset hole somewhere else. This is pretty clear. Quickly pressing the reset button quickly resets the router (quick/soft reset – does not wipe any settings). The reset hole is what you push a pin into for up to 20-30 seconds for the full reset until the lights on the front blink or go out (will wipe all settings and restore router to default).
It often looks something like this:
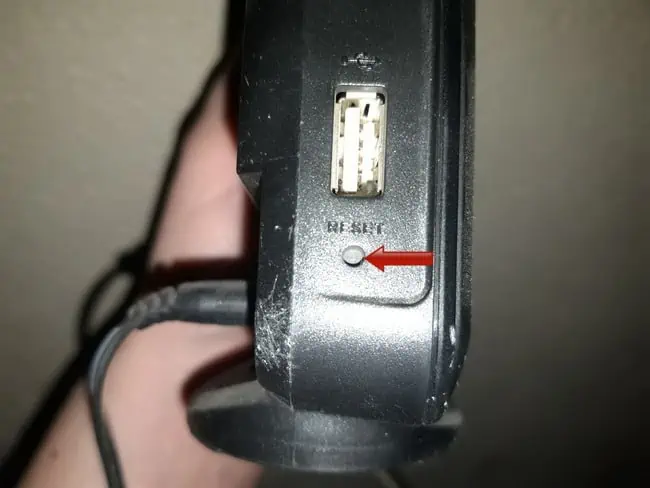

Pushing a bent safety clip or other sharp object into this hole for 5-30 seconds until something flashes/blinks is what does the factory reset. You might then need to wait up to 10 minutes for everything to reinstall and reboot.
This is a more extreme form of a reset; here’s what happens when you do a factory/default reset:
- All custom Wi-Fi SSIDs/usernames and passwords to access the network will be lost and reset to the defaults indicated on the sticker on the back of the router. So any users who need to reconnect will need to find the router again on the network list and re-enter the default password to use the Wi-Fi.
- If you have also set custom values for the router login admin/password (to change settings), these will also be reset back to the default values indicated on the sticker on the back.
- If any gamers have set a static IP for their console on the router, this will be deleted and they’ll have to do it again.
- Any other custom settings that were configured on the router (eg. QoS, DNS settings, DMZ) will be lost and need to be reconfigured.
- All logs and stored browsing history will be wiped off the router.
- Factory resets can sometimes also take longer than quick resets, with a disruption of connection for sometimes several minutes.
Contact Your ISP For Support
If you’ve tried literally everything we’ve covered here and are not getting anywhere, it’s best to contact your ISP for assistance. It may well be that the Wi-Fi equipment inside the router is broken and therefore a replacement needs sending out.
It might be a good idea to open up a live chat with your ISP, explain what the problem is and what steps you’ve tried, and take things from there.
Here are links to customer support pages to get you started for major ISPs in the English speaking countries:
- America:
- United Kingdom:
- Canada:
- Australia:
